The significance of patient safety in the modern operating room (OR) cannot be overstated. Every aspect of the surgical environment, from the equipment to the team of specialists, contributes to ensuring that patients undergo procedures in the safest conditions possible. One such often overlooked but crucial component in the OR is the positioning pad. These pads play an essential role in optimizing surgical positioning, which in turn minimizes risks associated with surgery, such as nerve damage, pressure ulcers, and positioning-related complications. This article explores the importance of positioning pads, how they function in the operating room, and the critical role they play in enhancing surgical safety.
The Significance of Patient Positioning in Surgery
Positioning a patient correctly during surgery is vital for both the success of the procedure and the patient’s well-being. The human body is made up of several structures that must be carefully managed to avoid unnecessary pressure or trauma during surgery. A proper surgical posture preserves the patient’s comfort and safety while guaranteeing the surgeon’s access to the surgical site.
However, prolonged periods in a specific position can place immense pressure on certain body parts, resulting in possible complications such as:
- Nerve injury: Compression of the nerves in specific places can cause either temporary or permanent harm.
- Pressure ulcers: Prolonged pressure on areas like the sacrum, heels, and elbows can result in painful sores that delay recovery.
- Blood circulation issues: Improper positioning may obstruct blood flow, leading to ischemia and other circulation-related problems.
- Musculoskeletal stress: Incorrect posture can cause pain or injury by putting tension on muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Positioning pads are designed to prevent or reduce these risks by providing the necessary support, cushioning, and stabilization to maintain an optimal position throughout the surgical procedure.
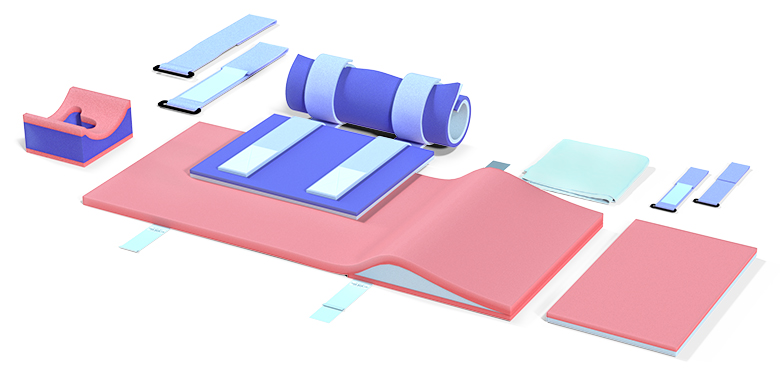
Types of Positioning Pads and Their Functions
Positioning pads come in a variety of forms and materials, each suited to different surgical positions and procedures. Some common types include:
- Head and Neck Positioning Pads: These pads are used to support and stabilize the head and neck, especially in procedures requiring supine, prone, or lateral positioning. For example, headrests may be used in neurosurgeries to ensure proper alignment and prevent cervical strain.
- Limb Positioning Pads: These are designed for use when a patient’s arms or legs are placed in specific positions for surgery. For instance, during shoulder surgery, a limb pad will help to elevate the arm in a safe and stable manner.
- Orthopedic Positioning Pads: These pads are typically used for orthopedic surgeries, where patients need to be positioned on their side or prone to access specific areas of the body.
- Heel Pads: Commonly used to prevent heel ulcers, these pads provide support to the heels when the patient is lying on their back or in a seated position.
- Specialty Positioning Pads: These pads are made to fit particular patient situations or procedures. For instance, bariatric positioning pads are used to accommodate patients with obesity, ensuring that their positioning remains safe and stable during surgery.
Each of these pads is designed to work in conjunction with the OR table and other supporting devices. The material of the pad plays an important role in determining its efficacy, as it needs to be firm enough to offer support but soft enough to minimize pressure.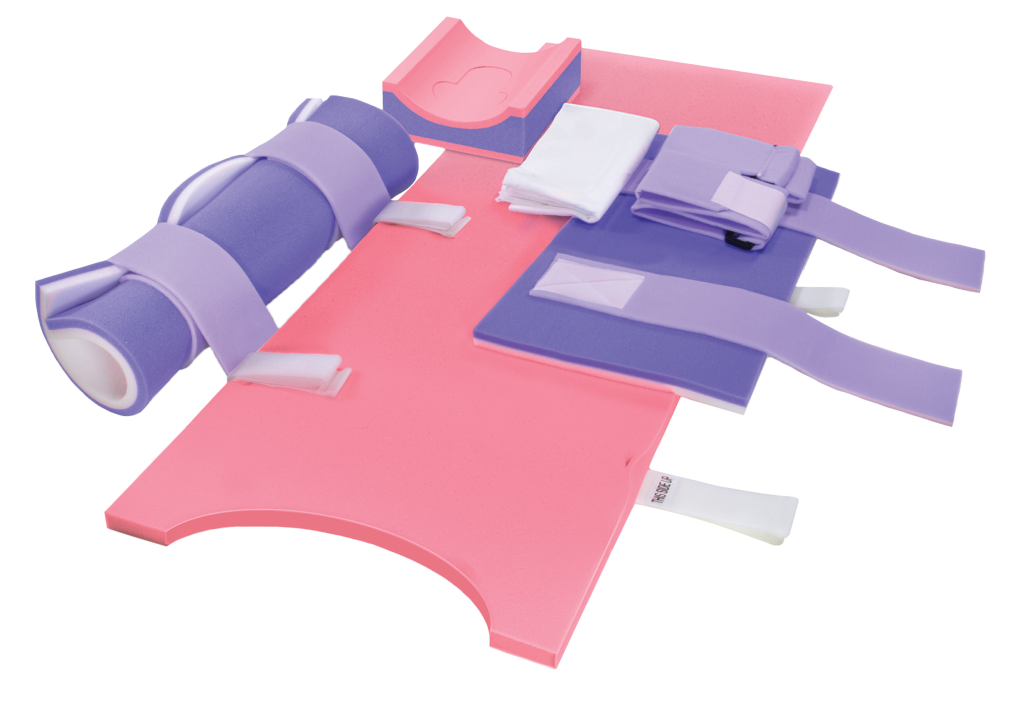
The Role of Positioning Pads in Reducing Pressure and Preventing Injuries
One of the most critical roles of positioning pads is the reduction of pressure-related injuries, such as pressure ulcers and nerve damage. These injuries are a common risk during surgery, especially when a patient is positioned in one position for an extended period.
Positioning pads help by evenly distributing pressure across the body. They create a buffer between the patient and the OR table, which helps to relieve localized pressure points that could otherwise lead to injury. By supporting areas such as the bony prominences (e.g., the heels, elbows, and sacrum), positioning pads reduce the chances of developing pressure ulcers, which can delay recovery and complicate the surgical outcome.
Furthermore, positioning pads can assist in maintaining proper body alignment, which ensures that no area of the body is subjected to undue strain. For example, during a back surgery, the use of a lumbar support pad can reduce pressure on the lower back and prevent potential musculoskeletal injuries. By properly aligning the patient’s spine and limbs, these pads help avoid nerve compression or injury that might occur in poorly positioned patients.
Enhancing Surgical Accuracy and Efficiency
The proper positioning of a patient not only enhances safety but also directly contributes to the accuracy and efficiency of the surgery. In order to offer the best visibility and access to the surgical site, several procedures call for a certain position or angle. Positioning pads support this need by allowing the surgical team to precisely adjust the patient’s body alignment.
For example, in spinal surgery, patients may need to be positioned in a prone position to allow access to the back. Positioning pads support the body in this position, ensuring that the surgeon has clear access to the spine while preventing any undue pressure on the patient’s chest or abdomen, which could interfere with breathing.
Similarly, in shoulder or hip surgeries, positioning pads help to maintain the limb in a stable, anatomically correct position, ensuring that the surgeon has the best possible access to the joint while minimizing any risk of unintended movements.
By improving access and maintaining stability during surgery, positioning pads reduce the chances of complications arising from poor positioning, such as accidental injury or surgical errors. This is crucial in procedures where precision is key, such as in neurosurgery or orthopedic surgery.
Minimizing the Risk of Post-Surgical Complications
Positioning pads not only help during the surgery itself but also play a significant role in minimizing post-surgical complications. Post-operative care often involves prolonged periods of bed rest or limited movement, during which the patient remains in the same position for extended hours.
Without proper cushioning and support, this can lead to a host of issues, including the development of pressure ulcers, circulatory problems, and even muscle stiffness. Using the correct positioning pads can help to prevent these complications by redistributing pressure and allowing for the patient to be repositioned without disrupting the surgical site.
For instance, in patients recovering from orthopedic surgery, positioning pads can help relieve pressure from the surgical site while maintaining optimal positioning for the healing process. This is especially important in procedures like hip replacements, where correct positioning helps ensure proper joint alignment during recovery.
The Impact of Technological Advancements in Positioning Pads
Positioning pads, like the majority of medical equipment, have changed as a result of advances in material science and technology. Advanced memory foam, gel-based materials, and viscoelastic polymers are frequently used to create modern positioning pads, which provide individualized support by conforming to the shape of the body.
Memory foam pads, for example, help to evenly distribute the patient’s weight, reducing localized pressure and improving comfort. Gel-based pads, on the other hand, offer superior cushioning and pressure relief and are often used in surgeries that require long durations in a single position. These new materials are more effective at preventing pressure ulcers and promoting healing, contributing to the overall safety and comfort of the patient.
In order to lower the danger of infection, many contemporary positioning pads are also made with antimicrobial qualities. These pads are simple to clean and disinfect, which lowers the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs), a leading cause of problems following surgery, and helps to keep the operating room sterile.
Conclusion
Positioning pads are an often-overlooked but vital component of the modern operating room. By providing support, cushioning, and stabilization, they help prevent a wide range of complications, from nerve damage to pressure ulcers, while enhancing surgical accuracy and efficiency. Their role in optimizing surgical position safety cannot be understated, as they directly contribute to patient comfort, minimize post-operative complications, and assist surgeons in performing procedures with precision.
The continuous improvement in materials and design ensures that positioning pads will remain a crucial part of the surgical environment, adapting to new surgical techniques and patient needs. As surgical procedures become more advanced and complex, the importance of positioning pads will only increase, highlighting their indispensable role in ensuring the safety and well-being of patients undergoing surgery.



