Proper patient positioning is essential in healthcare settings to enhance comfort, recovery, and overall well-being. Positioning pads, designed to support and maintain desired body positions, alleviate pressure, and prevent issues like pressure sores and muscle stiffness, are key tools in this process. This article will explore different types of positioning pads, their uses, benefits, materials, and how to select the right one for various patient needs.
What Are Positioning Pads?
Positioning pads, also known as positioning cushions, supports, or wedges, are devices used to help position the body in specific ways. These pads are typically made from materials that offer comfort, support, and pressure redistribution, and they are available in various sizes and shapes. Depending on the patient’s condition and needs, positioning pads can be used to:
- Support proper alignment of the body, minimizing stress on joints and muscles.
- Reduce pressure points that may cause pain or sores, improving comfort.
- Aid in the management of conditions like scoliosis, cerebral palsy, or post-stroke recovery, where specific body positioning is required for optimal health outcomes.
Positioning pads are commonly used in both acute care and rehabilitation settings. They are adaptable instruments for a variety of patients because they can also be used in home care settings.
Types of Positioning Pads and Their Applications
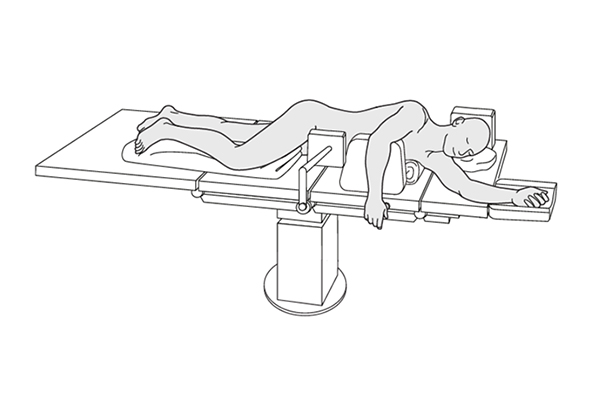
Lateral Positioning Pads
Lateral positioning involves placing the body on its side to reduce the risk of developing pressure ulcers on the back, buttocks, or heels. It is also beneficial for patients who need to improve lung function, relieve pressure on the heart, or assist in preventing aspiration pneumonia in people with swallowing difficulties. Lateral positioning pads are designed to provide support and stability when a patient is lying on their side.
Features:
- Wedge-shaped design to hold the body in a side-lying position.
- Adjustable to support the head, neck, shoulders, and hips.
- Soft foam or gel-filled options to reduce pressure on bony prominences.
Benefits:
- aids in reducing strain on the sacrum, which is where immobile people frequently develop pressure ulcers.
- Assists with postural alignment, especially in patients with conditions like scoliosis or cerebral palsy.
- Provides comfort and reduces muscle stiffness for patients who need to remain in a side position for extended periods.
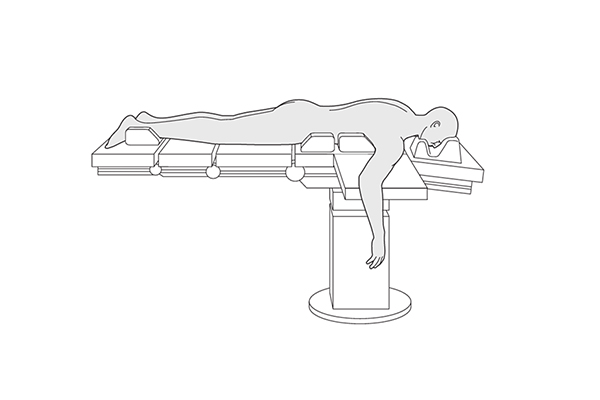
Prone Positioning Pads
Prone positioning involves placing a patient on their stomach. Patients with respiratory distress or COVID-19 who have trouble breathing will benefit most from this position. In physical therapy settings, it is also utilized to improve spinal alignment and ease back discomfort.
Features:
- Soft, cushioned pads are designed to provide comfort while lying prone.
- Often used in combination with pillows or foam wedges to support the head, torso, and legs.
- May feature cut-outs or channels to avoid pressure on the chest, abdomen, or face.
Benefits:
- Prone positioning helps optimize lung expansion and oxygenation, making it a useful intervention for patients with respiratory issues.
- Provides relief to the lower back, improving spinal alignment.
- Reduces pressure on certain areas of the body, such as the shoulder blades or rib cage, which are prone to discomfort during long periods of lying flat.
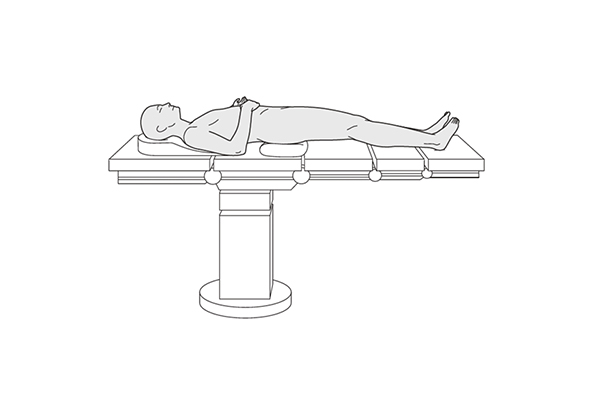
Supine Positioning Pads
Supine positioning involves placing the patient on their back. This is the most common body position for sleeping and resting. However, for those who are immobile or bedridden, using supine positioning pads is essential for ensuring comfort and preventing pressure sores on areas like the heels, sacrum, and elbows.
Features:
- Flat cushions or pads are designed to evenly distribute pressure across the body when lying on the back.
- Gel, foam, or air-filled materials to help redistribute body weight and minimize pressure on bony areas.
- Often includes specialized designs for supporting the head, shoulders, and hips.
Benefits:
- lowers the chance of musculoskeletal pain or scoliosis and encourages spinal alignment.
- Shifting weight away from high-risk regions including the sacrum, hips, and heels, helps avoid pressure ulcers.
- Makes individuals feel at ease and relaxed, whether they are recuperating from surgery or have limited movement.
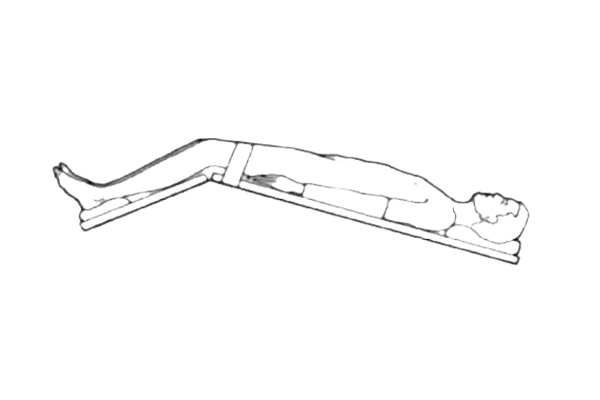
Trendelenburg Position
The patient must tilt their body such that their head is lower than their feet in order to assume the Trendelenburg posture. This position is often used in certain surgical procedures, especially to increase venous return, improve circulation, or in emergency settings where a patient is experiencing shock or low blood pressure. The Trendelenburg position may also be used to assist with drainage of abdominal or thoracic cavities.
Positioning Pads for Trendelenburg Position:
- Tilted Foam Pads: These pads are placed underneath the patient’s back to create the desired tilt. Foam pads can be shaped to provide the necessary elevation and ensure the body remains stable during this position.
- Leg Elevation Cushions: These are often used in combination with tilted pads to elevate the legs and stabilize the body while in the Trendelenburg position.
- Positioning Rolls: Rolls made from foam or gel may be placed under the feet or knees to help maintain the body at the correct angle and prevent discomfort.
Benefits:
- Helps improve blood circulation and venous return.
- Assists in specific medical procedures by promoting drainage.
- Reduces the risk of complications like swelling in the lower extremities.
Seated Positioning Pads
Seated positioning pads are designed to help individuals maintain an optimal seated posture. These pads are commonly used for patients who are sitting in wheelchairs, chairs, or other seated positions for extended periods. Proper seated positioning is essential for preventing pressure ulcers, ensuring proper circulation, and promoting comfort.
Features:
- Cushions with contoured shapes that support the thighs, buttocks, and lower back.
- Pads are made from memory foam or air-filled materials that conform to the body’s shape for optimal support.
- Adjustable to fit different types of seating, from wheelchairs to dining chairs.
Benefits:
- Helps lessen the strain on the tailbone and sit bones, which lowers the chance of developing pressure ulcers.
- Encourages good spinal alignment and posture, all of which are essential for avoiding back pain and discomfort.
- Enhances circulation by halting the formation of pressure sores on the thighs and buttocks.
Foot Positioning Pads
Smaller pads called foot positioning pads are used to support and cushion the feet. These pads are often used in patients who are bedridden or who have limited mobility, as they can help reduce foot drop, improve circulation, and alleviate pressure on the feet and ankles.
Features:
- Cushioned pads are designed to support the feet in an elevated or neutral position.
- Can be used to support the feet in a slightly flexed position, preventing the development of foot drop in patients with neurological conditions.
- Available in wedge, roll, or pillow shapes for various uses.
Benefits:
- Lowers the chance of contractures and foot drop while assisting in maintaining proper foot position.
- Relieves pressure on the heels and ankles, which are common sites for pressure sores.
- Enhances comfort and promotes circulation in the lower extremities, which is particularly important for individuals with limited mobility.
Pad Positioning for Particular Situations
Certain medical disorders cause certain people to have special needs. For example, patients with cerebral palsy, scoliosis, or spinal cord injuries may require specialized positioning pads to help support their bodies in specific ways. These specialized pads can help maintain posture, prevent deformities, and ensure comfort.
Features:
- Customized pads tailored to the patient’s condition, such as scoliosis or hemiplegia.
- Pads that assist in correcting posture or supporting a specific body part, such as the neck or legs.
- Often made with high-density foam or gel to provide targeted support.
Benefits:
- Helps maintain correct posture, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal problems.
- Provides comfort and pressure relief for patients with specialized needs.
- Enhances mobility and independence, allowing patients to engage in activities like sitting or standing for longer periods.
Material of Positioning Pads
The materials used in a positioning pad’s construction frequently determine how successful it is. Typical materials include the following:
- Foam: Soft and comfortable, foam is a popular material for positioning pads due to its ability to conform to the body. High-density foam provides better support, while memory foam offers more cushioning.
- Gel: Gel-filled pads provide excellent pressure relief by redistributing weight more evenly, making them ideal for preventing pressure sores.
- Air: Air-filled positioning pads, such as those used in alternating pressure mattresses, provide dynamic support and help reduce the risk of pressure ulcers.
- Viscoelastic materials: These materials combine the benefits of foam and gel, offering both support and comfort.
Conclusion
Positioning pads are essential for ensuring proper alignment and comfort, especially for patients with limited mobility or those who are bedridden or sitting for long periods. With a variety of options—such as lateral pads and foot cushions—they support different body positions, helping to prevent pressure sores, muscle stiffness, and poor circulation. Choosing the right pad improves comfort, enhances recovery, and reduces immobility-related risks, making them a key tool in quality patient care.